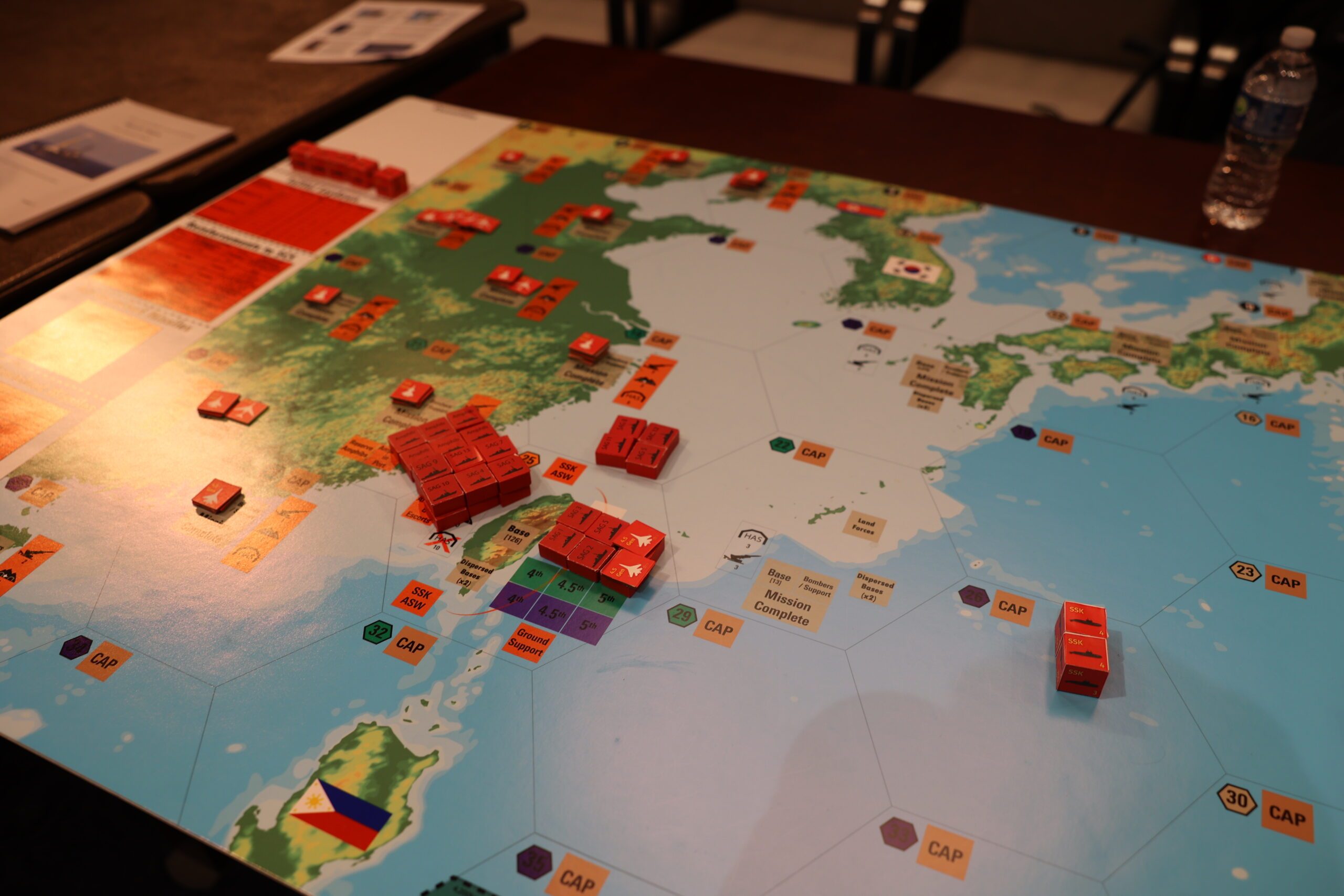
A latest simulation performed by the Middle for Strategic and Worldwide Research (CSIS) paints a stark image of the U.S. protection industrial base, revealing crucial vulnerabilities in its skill to assist army operations within the occasion of a large-scale battle. The findings underscore the pressing want for public-private partnerships, elevated funding in manufacturing capability, and lowered reliance on international parts.
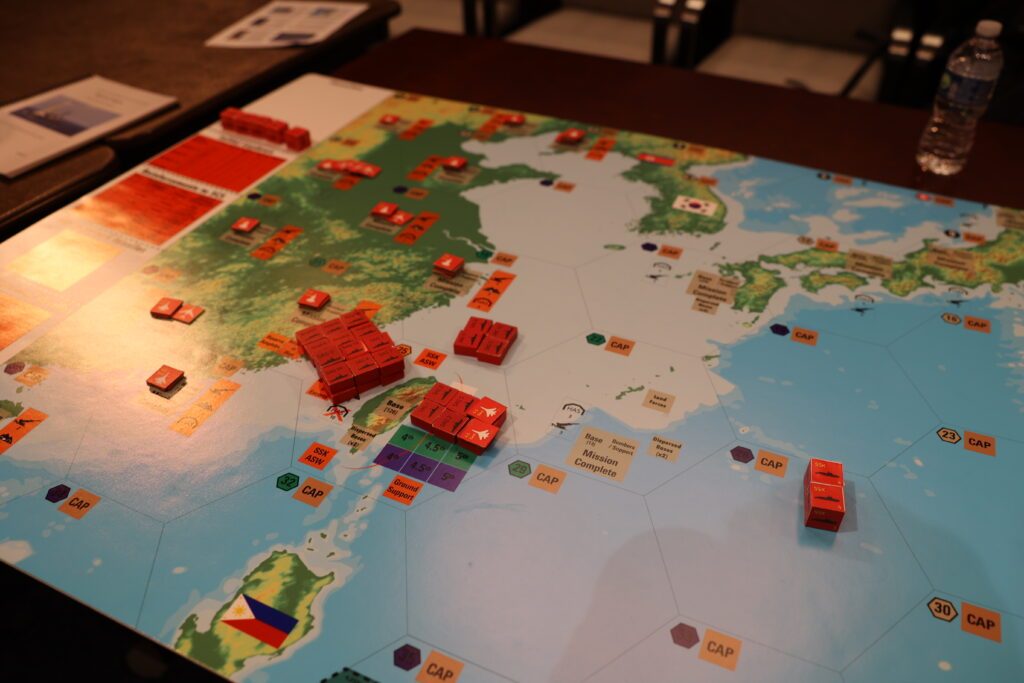


Rising World Tensions Expose Protection Shortcomings
The simulation, set in 2026, modeled a possible battle within the Indo-Pacific involving the US, Taiwan, Japan, and China. It highlighted the pressure on U.S. army sources on account of ongoing world crises, together with the Russo-Ukrainian Struggle, escalating tensions within the Western Pacific, and continued instability within the Center East. These simultaneous conflicts stretch the protection industrial base to its limits.
Key vulnerabilities recognized within the simulation embody:
- Crucial munitions shortages: Stockpiles of important munitions, akin to Lengthy-Vary Anti-Ship Missiles (LRASM) and Tomahawk missiles, can be depleted inside days of battle.
- Ship and plane losses: U.S. forces would endure heavy losses, together with plane carriers, floor ships, and fighter plane, with present manufacturing charges unable to replenish these belongings for years.
- Reliance on international parts: Crucial protection applied sciences, together with microelectronics, superior batteries, and different supplies, rely closely on imports, lots of which come from China.
A Protection Industrial Base Unprepared for Extended Battle
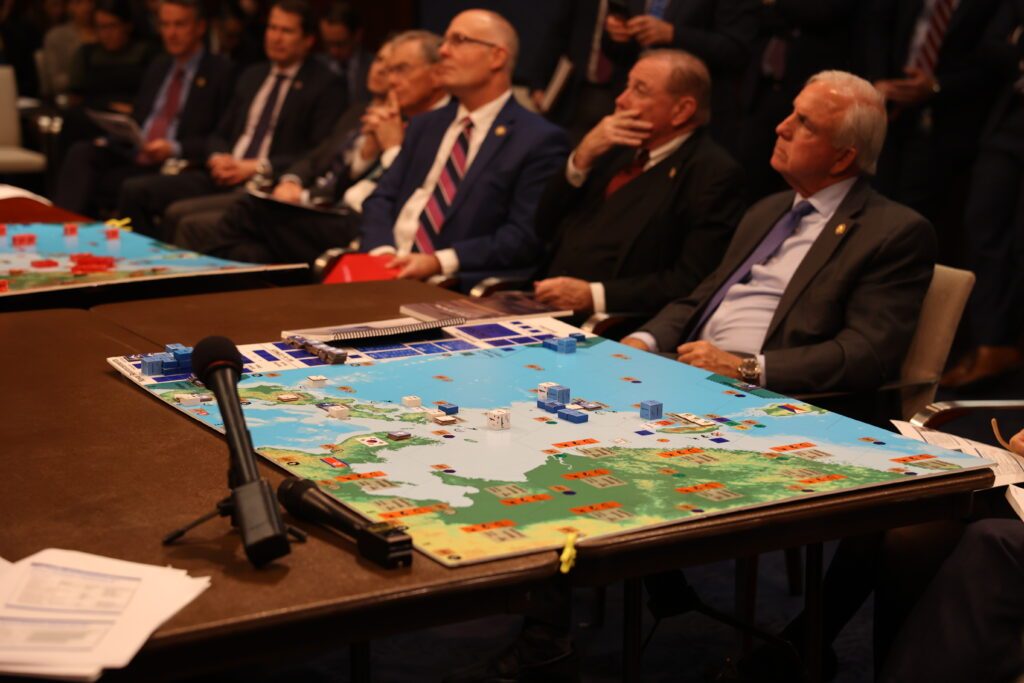


The simulation underscores that the U.S. industrial base, working largely on peacetime schedules, just isn’t geared up to maintain a protracted battle. For instance:
- Manufacturing timelines: Munitions akin to JASSM and Tomahawk missiles require as much as two years to provide, even underneath present circumstances.
- Provide chain fragility: The U.S. lacks home manufacturing capability for important parts, together with stable rocket motors, castings, and superior processors, creating dependencies that would grow to be crucial liabilities in wartime.
- Workforce shortages: An absence of expert staff, akin to engineers and metalworkers, contributes to delays within the manufacturing of ships, munitions, and different protection belongings.
Public-Non-public Partnerships: A Path Ahead
The CSIS report emphasizes the necessity for stronger public-private partnerships to deal with these deficiencies. By fostering collaboration between authorities businesses and personal producers, the U.S. can mobilize sources, scale manufacturing, and guarantee a extra resilient industrial base.
Key suggestions embody:
- Increasing manufacturing capability: Constructing new amenities and upgrading current ones to assist elevated manufacturing of crucial protection applied sciences.
- Lowering reliance on international parts: Growing home provide chains for important supplies akin to batteries, microelectronics, and superior alloys.
- Accelerating acquisitions and contracting: Adopting wartime procurement practices to streamline the supply of crucial protection belongings.
- Investing in workforce growth: Creating packages to coach and retain expert staff in crucial trades akin to shipbuilding, electronics, and munitions manufacturing.
Classes from the Simulation: A Name to Motion
The simulation highlights the implications of underinvestment within the protection industrial base. Inside weeks of a hypothetical battle, the U.S. would run out of key munitions, whereas its skill to exchange misplaced ships and plane can be severely restricted. In the meantime, China’s considerably bigger shipbuilding and manufacturing capability positions it to get better much more shortly from wartime losses.
Addressing these challenges requires not solely elevated funding but additionally a strategic shift in how the U.S. prepares for future conflicts. Public-private partnerships can play an important position in revitalizing the protection industrial base and making certain it will possibly meet the calls for of recent warfare.
Constructing a Resilient Industrial Base
The CSIS simulation serves as a wake-up name, demonstrating that the U.S. protection industrial base should transition from a peacetime to a wartime footing to stay aggressive in an more and more unstable world. These challenges lengthen to the drone business, which has struggles to develop home manufacturing on the identical scale as their international counterparts and to scale back reliance on international parts akin to batteries and microelectronics sourced from China. By prioritizing collaboration, lowering dependencies, and investing in home capabilities, the US can strengthen its place as a worldwide chief in protection and safety.
Need DRONELIFE information delivered to your inbox each weekday? Enroll right here.
Learn extra:
Miriam McNabb is the Editor-in-Chief of DRONELIFE and CEO of JobForDrones, an expert drone providers market, and a fascinated observer of the rising drone business and the regulatory atmosphere for drones. Miriam has penned over 3,000 articles centered on the industrial drone house and is a world speaker and acknowledged determine within the business. Miriam has a level from the College of Chicago and over 20 years of expertise in excessive tech gross sales and advertising and marketing for brand new applied sciences.
For drone business consulting or writing, E mail Miriam.
TWITTER:@spaldingbarker
Subscribe to DroneLife right here.