[ad_1]
Testing Transportable Airspace Administration Programs for Safer, Extra Efficient Aerial Firefighting
NASA is working with the wildfire response group to develop new applied sciences that may improve aerial firefighting operations, significantly at night time. These developments might allow drones, each remotely piloted and autonomous, to help in wildfire suppression across the clock, even in low-visibility circumstances.


Enhancing Aerial Firefighting with Autonomous Applied sciences
At the moment, aerial firefighting is proscribed to sunlight hours when pilots have clear visibility. Nighttime operations pose vital dangers resulting from potential collisions with terrain or different plane. To deal with this problem, NASA has been testing airspace administration applied sciences that enable drones and remotely piloted plane to function safely at night time.
In an article posted by NASA, the undertaking supervisor explains:
“We’re aiming to offer new instruments – together with airspace administration applied sciences – for 24-hour drone operations for wildfire response,” mentioned Min Xue, undertaking supervisor of the Superior Capabilities for Emergency Response Operations (ACERO) undertaking inside NASA’s Aeronautics Analysis Mission Directorate. “This testing will present helpful information to tell how we mature this expertise for eventual use within the subject.”
Introducing the Transportable Airspace Administration System (PAMS)
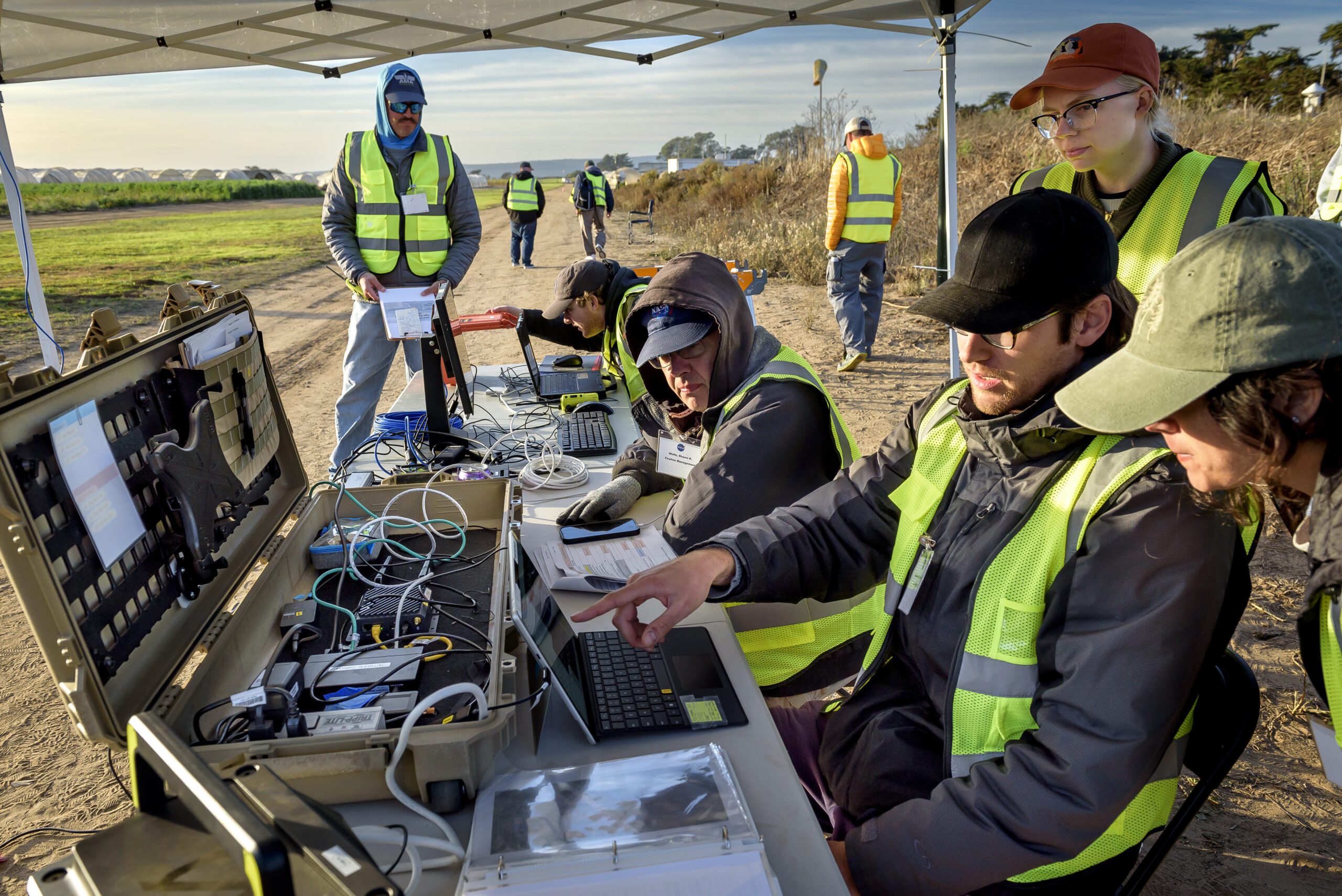


Over the previous 12 months, ACERO researchers have developed the Transportable Airspace Administration System (PAMS), designed to assist drone pilots safely deploy plane for wildfire response. Every PAMS unit, in regards to the measurement of a carry-on suitcase, is supplied with:
- A pc for airspace administration
- A radio for communication amongst PAMS items
- An Computerized Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) receiver to trace close by air site visitors
These elements are housed in a rugged, moveable container, making the system simply deployable within the subject. The PAMS software program helps drone pilots forestall airborne collisions by monitoring and sharing flight plans with different plane within the community. Moreover, it supplies important hearth location and climate info.
A key characteristic of the system is an airborne communication relay. A drone geared up with a communication machine serves as a relay between ground-based PAMS items, enabling communication with out counting on web connectivity.
Profitable Testing at A number of Areas
To guage PAMS’ effectiveness, NASA researchers carried out a collection of exams at varied places throughout the nation.
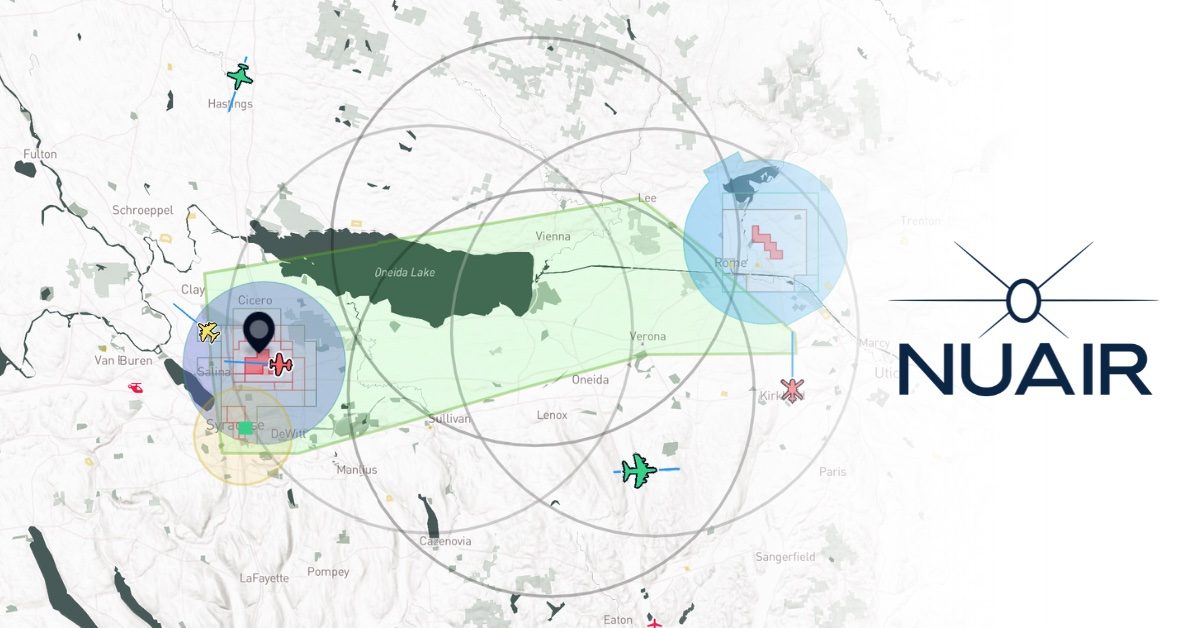
At NASA’s Ames Analysis Middle in California’s Silicon Valley, three PAMS items have been positioned in numerous places exterior one another’s line of sight. Researchers entered flight plans into every system and confirmed that the items efficiently shared info by a mesh radio community.
The group then expanded testing at NASA’s Langley Analysis Middle in Hampton, Virginia. An extended-range vertical takeoff and touchdown (VTOL) plane geared up with a digicam, laptop, mesh radio, and ADS-B receiver was flown alongside two smaller drones. These exams demonstrated that the mesh radio community aboard the bigger drone efficiently related with the small drones and a number of ground-based PAMS items.
Simulating Actual-World Firefighting Operations
Additional testing passed off at Monterey Bay Academy Airport in Watsonville, California, the place researchers simulated real-world firefighting situations. A winged VTOL drone by Overwatch Aero established a communications relay to 3 separate PAMS items. Two further drones have been flown close by, with pilots deliberately submitting conflicting flight plans and working exterior preapproved zones.
The PAMS items efficiently detected these conflicts, alerted pilots, and shared real-time plane location, climate updates, and simulated hearth location information. These outcomes recommend that PAMS can considerably enhance aerial coordination throughout wildfire operations.
“This testing is a major step in the direction of enhancing aerial coordination throughout a wildfire,” Xue mentioned. “These applied sciences will enhance wildfire operations, cut back the impacts of enormous wildfires, and save extra lives.”
Wanting Forward
The ACERO group plans additional flight evaluations this 12 months to refine these wildfire applied sciences. The last word aim is to switch the expertise to firefighting businesses to reinforce their operational capabilities.
This initiative is a part of NASA’s broader efforts underneath the ACERO undertaking, which operates inside the company’s Aeronautics Analysis Mission Directorate and helps the Superior Air Mobility mission.
For extra particulars on NASA’s ACERO undertaking, go to NASA. Extra info on Overwatch Aero will be discovered at Overwatch Aero.
Need DRONELIFE information delivered to your inbox each weekday? Enroll right here.
Learn extra:


Miriam McNabb is the Editor-in-Chief of DRONELIFE and CEO of JobForDrones, knowledgeable drone providers market, and a fascinated observer of the rising drone trade and the regulatory surroundings for drones. Miriam has penned over 3,000 articles targeted on the business drone area and is a global speaker and acknowledged determine within the trade. Miriam has a level from the College of Chicago and over 20 years of expertise in excessive tech gross sales and advertising for brand new applied sciences.
For drone trade consulting or writing, Electronic mail Miriam.
TWITTER:@spaldingbarker
Subscribe to DroneLife right here.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink